Bram Houghton
June 30, 2025
Commentary Weekly update Weekly commentaryMarket Update– June 16th – June 27th, 2025
MARKET UPDATE – June 16th – June 27th, 2025
In a Nutshell: Optimism continues globally as progress has been made on trade deals, which reduces the chances of tariffs, while soft inflation data in the U.S. increases the hope of rate cuts, despite the Fed reiterating a cautious approach. Globally, risk off trades and oil price volatility paused as tensions in the Middle East between Iran and Israel cooled as a ceasefire was announced.
Update - The U.S. announced negotiations with Canada would cease immediately due to the Digital Services Tax implementation.
U.S. Labour Markets
The U.S. labor market is showing signs of softening, with initial jobless claims falling to 236,000 for the week ending June 21, but continuing claims—a proxy for hiring—rising to 1.974 million, the highest level since November 2021.
Layoffs have increased amid economic uncertainty which presents planning challenges for businesses. Hiring remains tepid, and the unemployment rate is expected to rise to 4.3% in June from 4.2% in May. Consumer sentiment around job availability has also weakened, with the share of people viewing jobs as "plentiful" dropping to a four-year low.
Outlook: The U.S. labor market and broader economy are losing momentum, with rising layoffs, weaker hiring, and declining housing activity due to higher borrowing rates and tariff-related costs. While the Federal Reserve is holding rates steady for now, the risk of further economic softening could prompt rate cuts later in the year.
U.S. Economy
Economic growth in the U.S. is under pressure, with GDP contracting by an annualized rate of 0.5% in Q1 due to weaker consumer spending, exports, and government spending, compounded by trade disruptions from tariffs.
The goods trade deficit widened by 11.1% in May as exports declined, though a slowdown in imports may support GDP growth in Q2, which is forecasted to rebound at a 3.4% annualized rate.
Inflation remains a key concern, with tariff-related price increases expected to intensify in the coming months. Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell reiterated the central bank’s "wait-and-see" approach to interest rate changes, emphasizing data dependency as policymakers navigate these uncertainties.
Pending home sales in the U.S. rose by 1.8% in May, surpassing expectations, but persistently high mortgage rates (averaging 6.79%) and record-high home prices are straining affordability. New home sales fell sharply to indicating a potential slowdown.
Outlook: The U.S. economy faces headwinds from high mortgage rates, slowing housing activity, trade disruptions, and weaker industrial and retail performance. While the labour market remains stable, inflationary pressures and geopolitical uncertainties weigh on consumer sentiment and economic growth. The Federal Reserve is maintaining a cautious stance, awaiting clearer signals from inflation and trade developments.
Canadian Economy
Canada's annual inflation rate remained steady at 1.7% in May, with declining gasoline prices helping to stabilize the overall index. Prices for shelter, food, and transportation also cooled, though core inflation measures like the weighted-median CPI (2.2%) and trimmed mean CPI (2.8%) suggest inflationary pressures persist.
Economists believe the Bank of Canada will remain cautious, awaiting further data, including GDP figures, before considering rate cuts. A material economic slowdown in April or May could open the door to easing, but stable inflation and resilient GDP growth would likely rule out such measures.
Retail sales in Canada rose by 0.3% in April, driven by gains in motor vehicle and parts sales. However, core retail sales (excluding autos and gasoline) edged up just 0.1%, reflecting subdued discretionary spending. Preliminary data for May indicate a potential 1.1% decline in retail sales, signaling a weaker start to the summer for the retail sector.
Outlook: Canada's inflation remains stable at 1.7%, but core inflation pressures persist, keeping the Bank of Canada cautious on rate cuts. Retail sales showed modest growth in April, driven by auto sales, though early data for May suggest a potential pullback, reflecting ongoing economic uncertainty.
UK Economy
Retail sales volumes fell sharply by 2.7% in May, marking the steepest monthly decline since December 2023, as demand cooled following April's spending surge on food, summer clothing, and home improvements. Inflation eased slightly to 3.4% in May but remains above the Bank of England's 2% target, with services price inflation proving "sticky." The manufacturing sector reported its sharpest contraction in orders since January, driven by weak domestic demand, though export orders showed resilience. Grocery price inflation rose to 4.7%, adding pressure on low-income households, while discretionary spending remained subdued.
Despite these challenges, the UK economy grew by 0.7% in Q1 2025 but contracted in April due to the end of a property tax break and the impact of U.S. tariffs. The Bank of England forecasts 1% growth for 2025 and is expected to hold interest rates steady at 4.25%.
Outlook: The UK is grappling with weak retail sales, persistent inflation, and a contracting manufacturing sector, though export resilience and modest consumer spending may provide some support.
Eurozone
In the EU economic activity remained subdued, with the eurozone's composite PMI holding at 50.2 in June, barely above the threshold for growth. Manufacturing continued to contract, while services activity showed only marginal improvement. Inflation fell below the European Central Bank's 2% target in May, with countries like Germany and France reporting subdued price pressures. Trade data revealed a widening goods trade surplus with the U.S., despite ongoing tariffs, but exports to China declined for the ninth consecutive month.
Spain's economy grew in Q1, while France is expected to see sluggish growth for the year, weighed down by weak manufacturing and modest consumer spending. The European Central Bank has signaled a pause in policy easing as inflation moderates.
Outlook: The economy is stagnating, with manufacturing under pressure and inflation easing below target, though trade with the U.S. and modest growth in countries like Spain offer some positive signals.
Energy
The latest reports from the Energy Information Administration (EIA) and the American Petroleum Institute (API) highlight significant developments in the energy markets. Natural gas storage increased, slightly below forecast, signaling stronger-than-expected demand and a bullish outlook for natural gas prices.
In the crude oil market, EIA data revealed a substantial drop in U.S. crude oil inventories, far exceeding the forecast, with this sharp decrease indicating heightened demand and a bullish outlook for crude oil prices.
Outlook: Natural gas markets are experiencing mixed signals, with fluctuating storage levels suggesting alternating bullish and bearish trends. Meanwhile, crude oil inventories have seen significant declines, pointing to strong demand and a bullish outlook for crude prices, though recent data hints at a potential slowdown. These developments have broad implications for energy prices, inflation, and economic conditions in both the U.S. and Canada.
Reuters Market Updates http://www.reuters.com
Bloomberg Market Updates - https://www.bnnbloomberg.ca/markets
| Market Data | S&P/TSX | S&P 500 | DOW | NASDAQ | STOXX EU | WTI | GOLD |
| Last Week | -0.4% | -2.6% | -2.5% | -2.5% | -0.9% | -1.5% | 5.6% |
| This Week | 1.1% | 1.9% | 1.6% | 2.0% | 0.6% | -1.2% | -1.6% |
Market data taken from https://www.marketwatch.com/
One Big Beautiful Bill approaching deadline… by David Morgan, Reuters Investing.com
The U.S. Senate is facing intense political battles over President Donald Trump’s proposed "One Big Beautiful Bill Act," a sweeping tax-cut and spending package that Republican leaders aim to pass before the July 4 holiday.
While Senate Majority Leader John Thune and House Speaker Mike Johnson are pushing for swift passage, the bill has sparked divisions within the Republican Party. Hardline fiscal conservatives are demanding deeper spending cuts to address the $2.8 trillion increase in the federal deficit projected by the Congressional Budget Office (CBO), while other lawmakers oppose provisions that would reduce Medicaid funding and impact social programs.
The bill’s deficit impact could rise to $3.4 trillion when accounting for higher interest payments, contradicting Republican claims that tax cuts would pay for themselves through economic growth.
The legislation’s fate hinges on the Senate parliamentarian’s decision on whether it qualifies for privileged status to bypass the 60-vote filibuster and pass with a simple majority. Some Republicans, including Senators Ron Johnson, Mike Lee, and Rick Scott, are pushing for more time to negotiate additional savings, particularly from green tax credits and Medicaid. Meanwhile, Senate Democrats, led by Chuck Schumer, have criticized the bill for cutting healthcare, raising costs for middle-class families, and benefiting the wealthy.
U.S. Congress partisan polarization has intensified
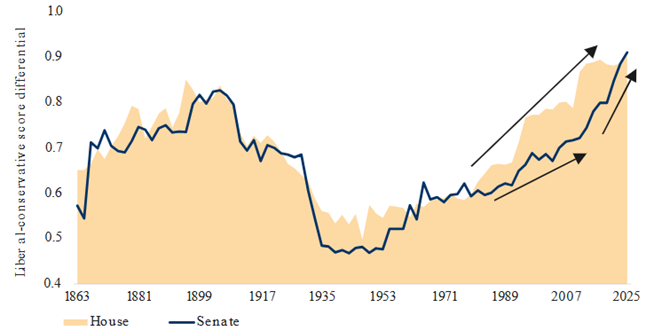
As of 06/16/2025. Measured as the difference between median scores for the Democratic and Republican members in the House of Representatives and Senate. Sources: Voteview.com, RBC GAM
Summary: President Trump’s tax-cut and spending bill faces significant resistance within the Republican Party over its projected $2.8 trillion deficit increase and controversial Medicaid cuts. While GOP leaders push for quick passage, fiscal conservatives demand deeper savings, and Democrats criticize the bill for favoring the wealthy at the expense of healthcare and middle-class families. The bill’s success depends on overcoming internal divisions and securing procedural approval in the Senate.
RBC GAM Macro Memo – June 17th – July 7th by Eric Lascelles, Chief Economist Link to Article
Economic fears are fading… but economic data now weakening
The global macroeconomic outlook has improved slightly as the worst-case tariff scenarios have not materialized, and initial economic damage has been less severe than anticipated. Consensus GDP growth forecasts for 2025 have been revised upward globally, reflecting rebounding business and consumer sentiment.
Metrics such as the Small Business Confidence Index and the CEO Confidence Index have shown improvement, while consumer confidence, including social media-based measures, has risen to optimistic levels.
U.S. consumer sentiment revived on Trump tariff pause
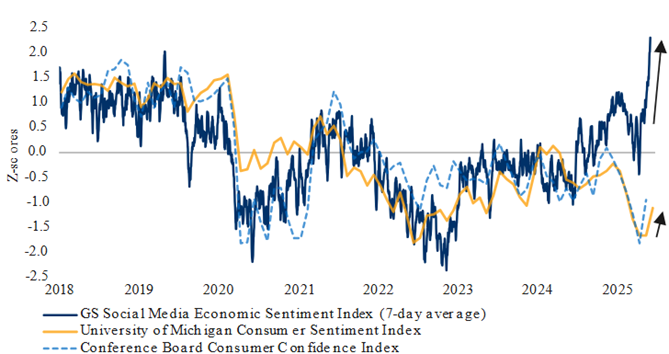
GS Social Media Economic Sentiment Index as of 05/30/2025, University of Michigan Index as of June 2025, Conference Board Index as of May 2025. Sources: Goldman Sachs Global Investment Research, University of Michigan, The Conference Board, Macrobond, RBC GAM
However despite these positive signals, underlying economic data in the U.S. is beginning to show some signs of weakness. Indicators such as downward payroll revisions, rising jobless claims, and the deteriorating Economic Surprise Index suggest softening economic momentum. The Federal Reserve’s Beige Book also reported declines in activity across half of its districts and reduced labor demand.
U.S. economic data have been deteriorating since Trump inauguration
As of 06/16/2025. Sources: Citigroup, Bloomberg, RBC GAM
Summary: While global GDP growth forecasts for 2025 have improved and sentiment is rebounding, U.S. economic data is showing early signs of weakness, with rising jobless claims and softening activity. Inflation remains subdued but could rise modestly in the coming months. The Federal Reserve is expected to maintain a cautious stance, revising its forecasts but holding off on immediate rate cuts, while markets anticipate gradual monetary easing over the next two years.
A new front opens in trade war
The Trump administration’s proposed Section 899, part of a broader House budget bill, introduces retaliatory taxes on foreign investment in the U.S. from countries deemed "discriminatory". This includes global minimum tax measures, Undertaxed Profits Rules (UTPRs), and significant to Canada, Digital Services Taxes (DSTs).
If enacted, Section 899 would increase withholding taxes on dividends repatriated to foreign parent companies, corporate profits, and certain inter-company transactions, as well as portfolio investment dividends. These measures aim to pressure countries to abandon tax policies perceived as disproportionately targeting U.S. multinational enterprises (MNEs).
However, the policy risks discouraging foreign direct investment (FDI) in the U.S., which is critical to the economy (accounts for 6% of private jobs, 7% of business-sector GDP) could erode returns, reduce foreign investment, and weaken demand for U.S. dollars, potentially undermining economic growth.
Implications for Canada
Canada is likely to be labeled a "discriminatory foreign country" due to its Digital Services Tax Act, which imposes a 3% tax on digital services revenue exceeding C$20 million. Under Section 899, withholding taxes on dividends paid to Canadian parent companies (currently taxed at a 5% treaty rate) and individual investors (15%) could rise to as high as 50% (5% each year over the next 10 years), significantly increasing costs for Canadian entities investing in the U.S. This would not be deductible from Canadian tax liabilities, amplifying the financial burden.
While Canada’s Global Minimum Tax Act is unlikely to trigger U.S. retaliation due to the absence of UTPRs, the DST remains a contentious issue. Canada may remove its DST during trade negotiations with the U.S., as the potential costs of Section 899 far outweigh the revenue generated by the tax, estimated at $3 billion annually.
As of June 27th, the U.S announced it would cease all trade negotiations with Canada due to the intended implementation of the DST.
Many countries have at least one “unfair” foreign tax
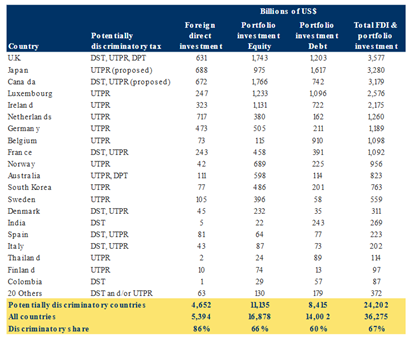
As of 06/11/2025. Sources: U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, PricewaterhouseCoopers, Tax Foundation, RBC GAM
Summary: Section 899 threatens to increase taxes on foreign investment in the U.S., potentially discouraging FDI and weakening economic growth. For Canada, the retaliatory measures could significantly raise costs for Canadian investors, particularly due to its DST. Canada may be compelled to remove its DST during trade negotiations to avoid the substantial financial impact of Section 899, which could cost several times the revenue generated by the tax. As of June 27th, the U.S. has escalated rhetoric targeting the DST directly.



